

The empirical rule is a quick way to get an overview of your data and check for any outliers or extreme values that don’t follow this pattern.įor non-normal distributions, the standard deviation is a less reliable measure of variability and should be used in combination with other measures like the range or interquartile range.

Around 99.7% of scores are between 20 and 80.Around 95% of scores are between 30 and 70.Around 68% of scores are between 40 and 60.The data follows a normal distribution with a mean score of 50 and a standard deviation of 10. Around 99.7% of scores are within 3 standard deviations of the mean.Įxample: Standard deviation in a normal distributionYou administer a memory recall test to a group of students.Around 95% of scores are within 2 standard deviations of the mean,.Around 68% of scores are within 1 standard deviation of the mean,.
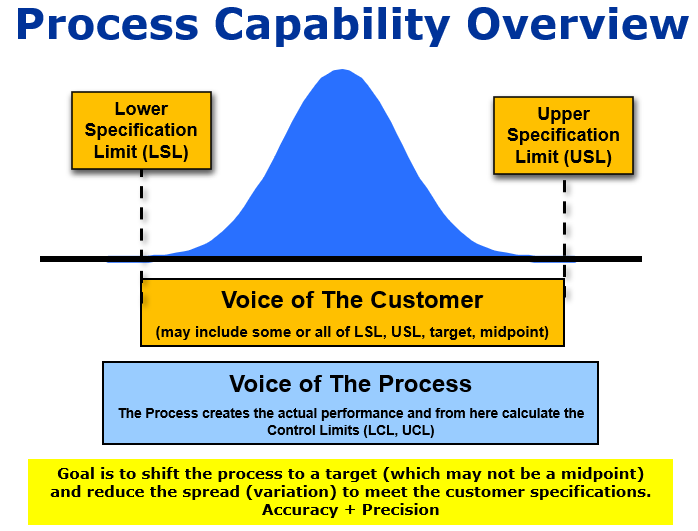
The empirical rule, or the 68-95-99.7 rule, tells you where your values lie: The standard deviation and the mean together can tell you where most of the values in your distribution lie if they follow a normal distribution. The curve with the lowest standard deviation has a high peak and a small spread, while the curve with the highest standard deviation is more flat and widespread. The standard deviation reflects the dispersion of the distribution. However, their standard deviations ( SD) differ from each other. The mean ( M) ratings are the same for each group – it’s the value on the x-axis when the curve is at its peak. Example: Comparing different standard deviationsYou collect data on job satisfaction ratings from three groups of employees using simple random sampling. When you have the standard deviations of different samples, you can compare their distributions using statistical tests to make inferences about the larger populations they came from. Many scientific variables follow normal distributions, including height, standardized test scores, or job satisfaction ratings. The standard deviation tells you how spread out from the center of the distribution your data is on average. Most values cluster around a central region, with values tapering off as they go further away from the center. In normal distributions, data is symmetrically distributed with no skew. Standard deviation is a useful measure of spread for normal distributions.

Why is standard deviation a useful measure of variability?.Steps for calculating the standard deviation.Standard deviation formulas for populations and samples.This is a very important component of Delta E, being the standard measurement tool to measure the difference (Delta E) between the colors represented (displayed) and the deviation from the true color location on the CIELAB scale. This scale gives a precise value with each value having a specific point on the scale, creating that particular hue of color. Each color is then a measure of their a*, b* and L* values, giving a definitive point of reference on the color scale. The horizontal plane is depicted with values of either +a/-a (which depicts a shift towards red/green respectively) and +b/-b (depicts a shift towards yellow/blue respectively). neutral grey L*=50) being the vertical center of the sphere. The scale is spherical by nature with white (i.e. With a lightness scale vertically in the center, colors can then be expressed with single values.Īs stated previously, this model is the standard and is represented by a color plotted-diagram with L* denoting lightness, a* denoting the red/green values and b* denoting the yellow/blue values. To address these issues, in addition to finding accepted tolerance levels, CIELAB can be used to scale, with the underlying theory being no two colors can be both red and green nor blue and yellow at the same time. The Comission Internationale de l’Eclairge (International Commission on Illumination) or CIE, has established Delta E as the standard color distance metric, revising past definitions to incorporate the human eye being more sensitive to certain colors. Generally speaking, the lower the Delta E number, the closer the display matches the input color to the display’s reproduced color. This standard quantifies this difference and is used to calculate the deviation from the benchmark standards which allows a tolerance level to be set (based on L*a*b coordinates). ViewSonic’s Delta E ≦2 color accuracy means superior, accurate color reproduction, achieving better than the eye can see color difference.ĭelta E is the standard calculation metric which correlates the human visual judgment of differences between two perceived colors.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
